EGP Outlook and Strategy
Published on - 21st March 2024
Egypt’s Economic Challenges and Reforms: A Comprehensive Overview
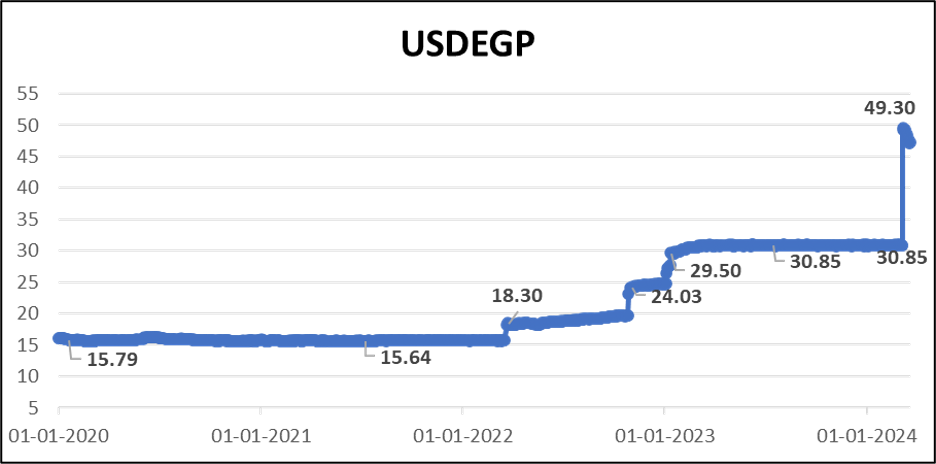
Currency Devaluation and Debt Sustainability Concerns – Egypt has grappled with significant economic challenges, including a drastic devaluation of the Egyptian pound against the dollar since March 2022. Rising interest rates and a weakening currency have escalated concerns about debt sustainability, with the ratio of interest costs to government revenue nearing 50%, and the debt-to-GDP ratio approaching 100%. The country faces daunting debt repayment schedules, with at least $42.26 billion due in 2024, including substantial amounts owed to international bodies like the IMF.
Social and Economic Strains – Social and economic strains have exacerbated Egypt’s financial woes. The pandemic has intensified poverty levels, with an estimated 60% of the population hovering around or below the poverty line. Unemployment, while declining slightly, remains a concern, alongside labor market participation issues and challenges in the public education system. A shortage of dollars has led to suppressed imports, driving up prices of essential goods and harming local industries.
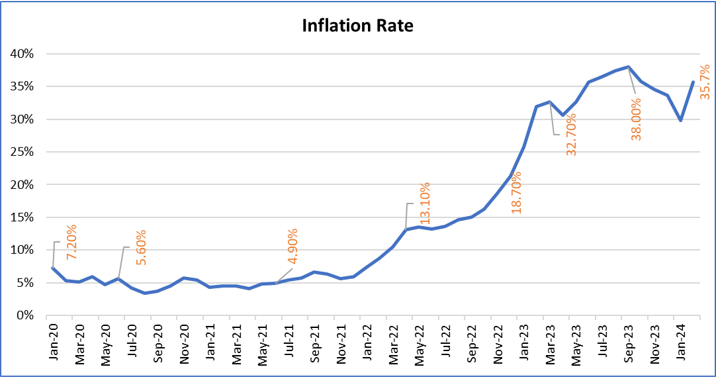
Structural Weaknesses and Monetary Challenges – Decades of poor planning and bureaucracy, along with historically overvalued currency and heavy borrowing, have contributed to Egypt’s economic woes. The country’s monetary challenges, including an increase in the money supply to finance deficits, have resulted in currency depreciation and soaring inflation rates. Fiscal measures to manage deficits, such as increasing prices of subsidized goods, have been largely ineffective against rising inflation.
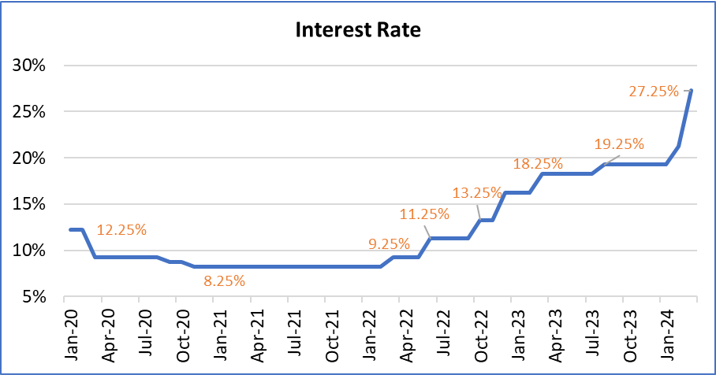
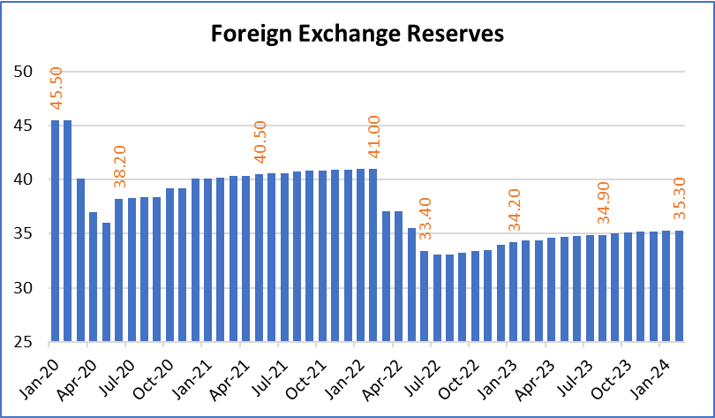
Recent Developments and Outlook – Despite these challenges, recent developments offer a glimmer of hope for Egypt’s economy. The central bank’s decision to raise key interest rates and secure an $8 billion IMF loan have stabilized the currency to some extent. Furthermore, Egypt’s bonds have become attractive to investors, offering high yields in emerging markets. With support from the IMF, the UAE, the World Bank, and the EU, Egypt aims to address its budget and balance of payments deficits and attract global capital. Although short-term challenges persist, the country’s financial outlook is gradually improving.
Current Account and Trade Dynamics – In the third quarter of 2023, Egypt experienced a widening current account deficit, despite a previous surplus. However, the services surplus, driven by growth in Suez Canal transit receipts and tourism revenues, has offered some respite. The trade balance deficit rose in December 2023, with a decrease in both exports and imports. While crude oil exports increased, natural gas and oil products exports experienced declines. Remittances from Egyptian workers abroad and net foreign direct investment inflows also decreased, adding further strain to Egypt’s economic landscape.
Outlook – Despite the economic challenges Egypt faces, recent financial agreements and support from global institutions suggest a promising outlook. EGP’s devaluation to meet IMF conditions may stabilize, with expectations of remaining pegged within a narrow range. With continued support and reforms, Egypt aims to address its fiscal imbalances and attract much-needed investment, positioning itself for sustainable economic growth in the future. Expect USDEGP to be rangebound between 46-49